What are SERP Features?
SERP features are unique elements that appear on Google’s search engine results page (SERP) that go beyond the traditional “10 blue links”. Common examples of SERP features include Featured Snippets, Knowledge Panels, video carousels and image packs.
These bells and whistles answer questions directly, showcase rich visuals, and offer quick access to specific information.
Here is a list of the most common SERP features (we’ll dive into each in more detail later):
- Featured Snippets: Concise answers pulled from websites, displayed above organic results.
- Top and Bottom Ads: Traditional text-based advertisements displayed at the top or bottom of search results.
- Video Carousels: Rotating or swipeable collections of video results relevant to your search.
- Rich Snippets: Enhanced information like reviews, ratings, and recipe ingredients directly in search results.
- Sitelinks: Additional links to specific pages within a website displayed under the main result.
- People Also Ask: Related questions and answers directly below the main search result.
- Local Pack: Map and listings for local businesses relevant to the search query.
- Knowledge Panels: Informative boxes about entities like people, places, and things.
- Image Packs: Grids of thumbnails showcasing visually relevant images related to your query.
- Twitter Cards: Rich media snippets from Twitter accounts displayed within search results.
- Top Stories Carousel: Rotating carousel of news stories relevant to the query.
In short:
A SERP without any SERP features looks like this:

And one with SERP features looks like this:

How Common are Google SERP Features?
It’s extremely rare to find a set of Google results without any SERP features.
According to SEMRush Sensor data, only 2.68% of Google’s first page results are without SERP features of any kind.

Which is why it’s important to take SERP features into account when choosing keywords and optimizing your content for organic CTR.
11 Most Important SERP Features
Here are the 11 most common SERP Features that appear in Google. These also tend to have a significant impact on how people interact with Google’s search results.
1. Featured Snippets
Featured Snippets are large boxes that highlight a specific section of a webpage. And present that section inside of the results themselves.

Featured Snippets usually appear at the very top of the page (below the ads).
But Google has recently started mixing Featured Snippets into the search results. For example, you can see here that the Featured Snippet essentially takes up the traditional #2 ranking position.

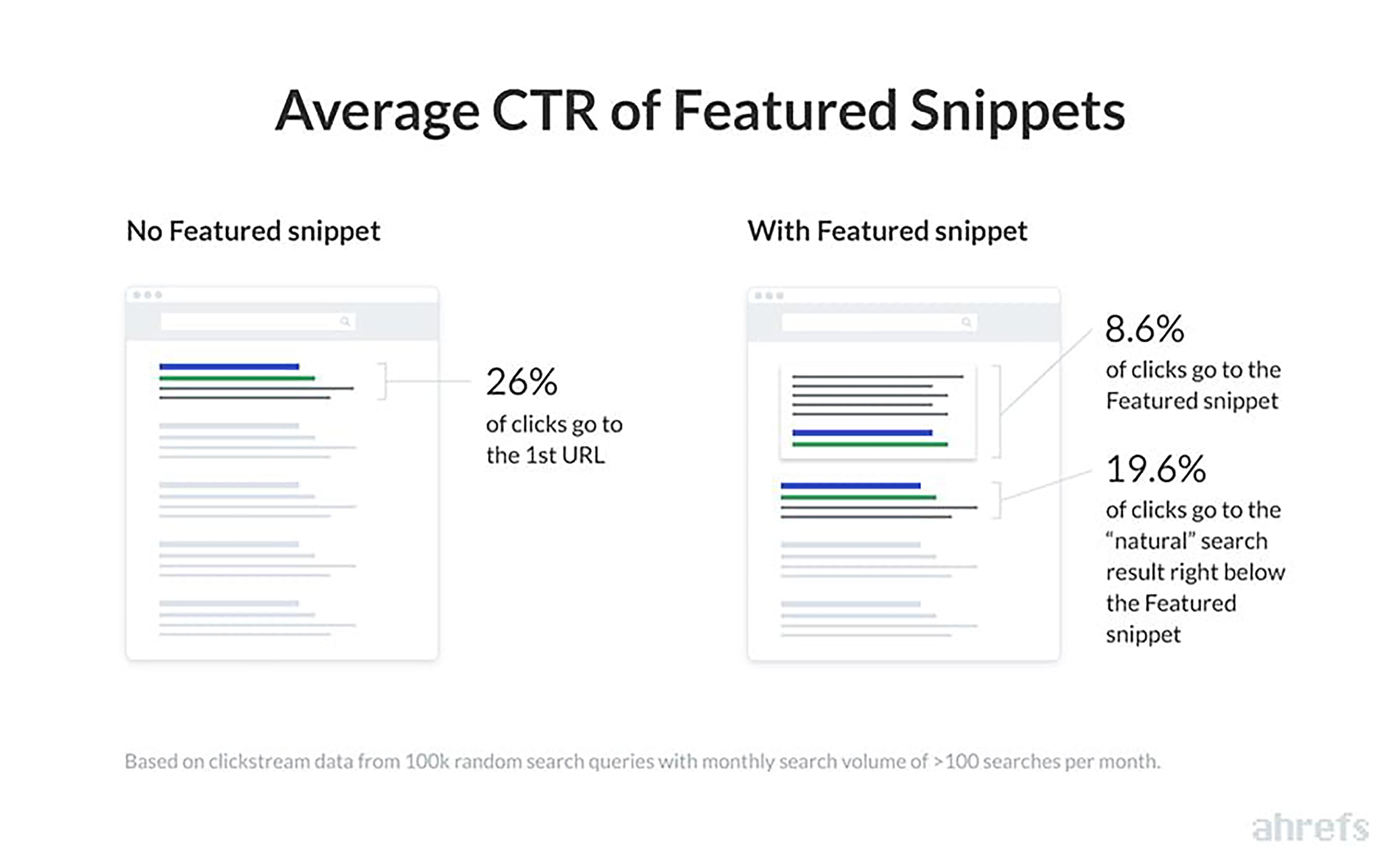
Featured Snippets have a significant impact on organic click through rate. Ahrefs discovered that the Featured Snippet gets about 8% of all organic clicks.
2. Top and Bottom Ads
This is fairly straightforward.
Google’s SERPs have two main Google Ads advertising slots:
One at the very top of the page (above the organic results). And another at the bottom of the page.
Wordstream data shows that the average CTR for a Google ad is about 3%. So ads definitely impact organic CTR. But much less so than Featured Snippets.
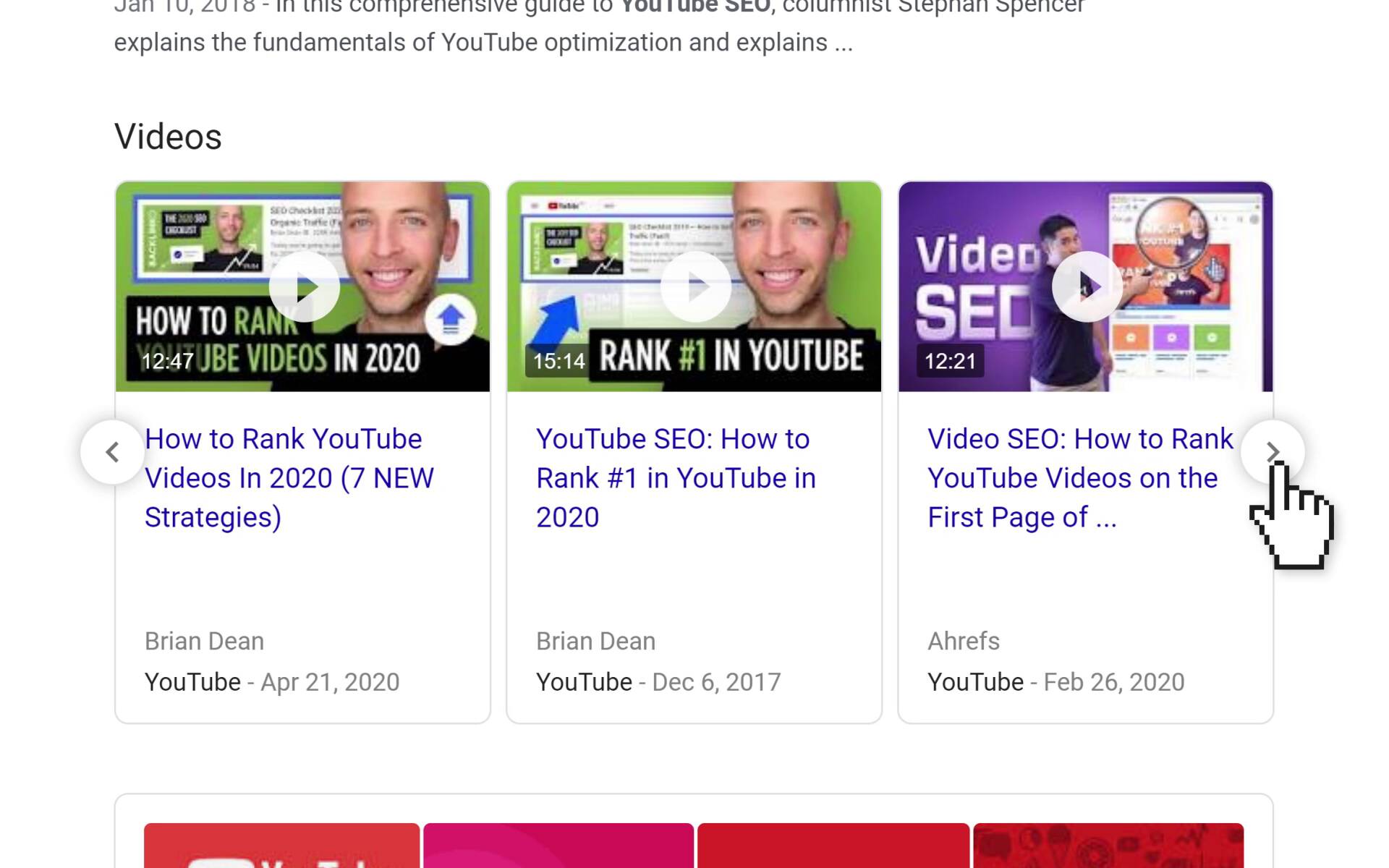
3. Video Carousels
Video carousels are a set of video results (usually pulled from YouTube) that appear in the results.
Here’s an example:
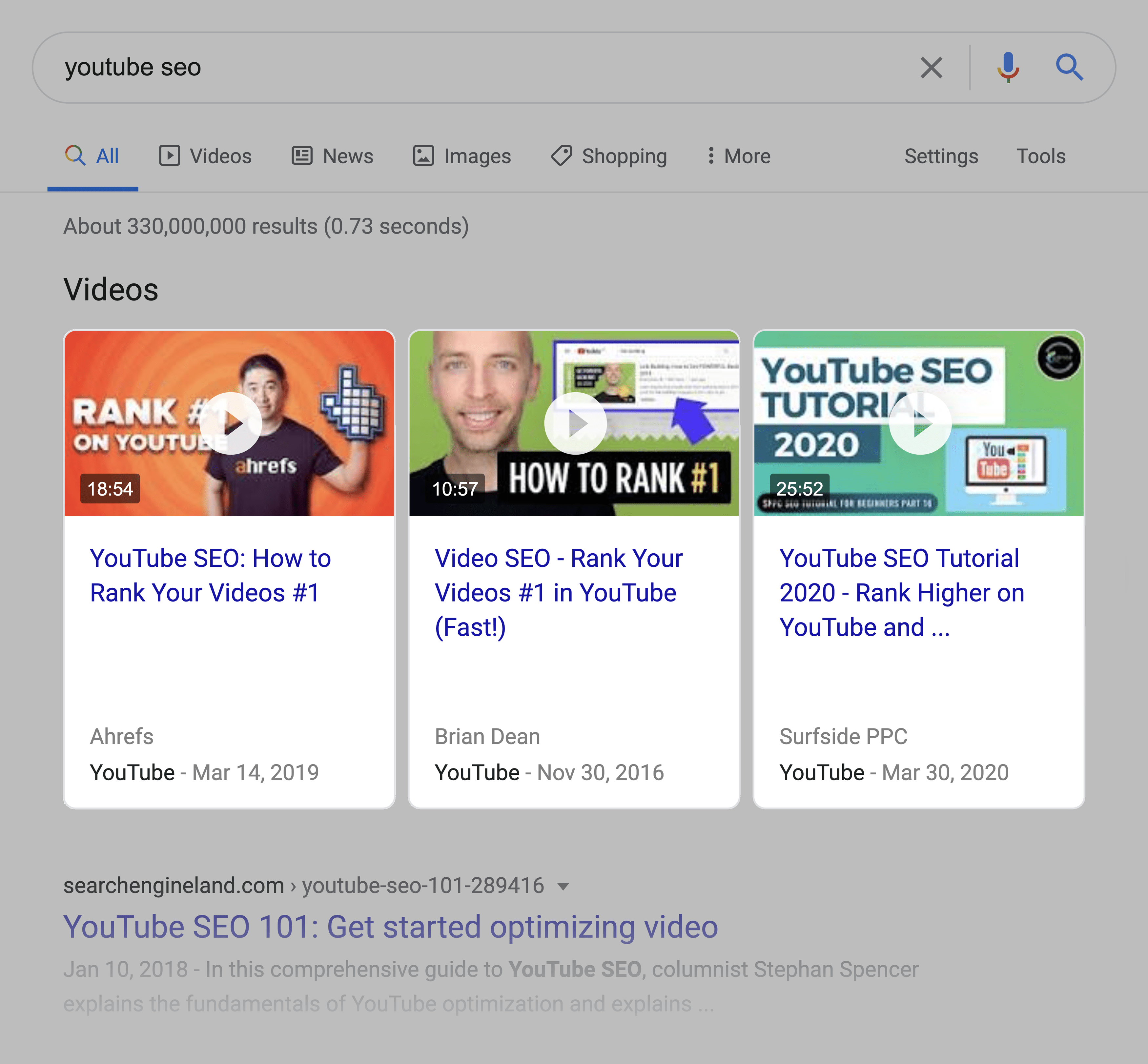
This used to be a static set of 3 results. But today, you can actually click the little arrow button to see more video results (up to 10 total).
Google doesn’t show video results for most search queries.
(In fact, SEMrush estimates that only about 6% of searches bring up a video result).
That said, video carousels are significant because they take up a lot of SERP real estate. Plus, they often appear at or near the top of the page. Which makes people more likely to click on them.
4. Rich Snippets
Rich snippets are extra pieces of information that appear next to one specific result.
They’re basically SERP features for a specific result in the SERPs.
As you probably know, most Google results are made up of a title tag, a description and a URL.
Well, rich snippets add additional information that goes well beyond those 3 elements.
Which helps users decide whether or not to click on it.
For example, certain results show price and availability information as a rich snippet.
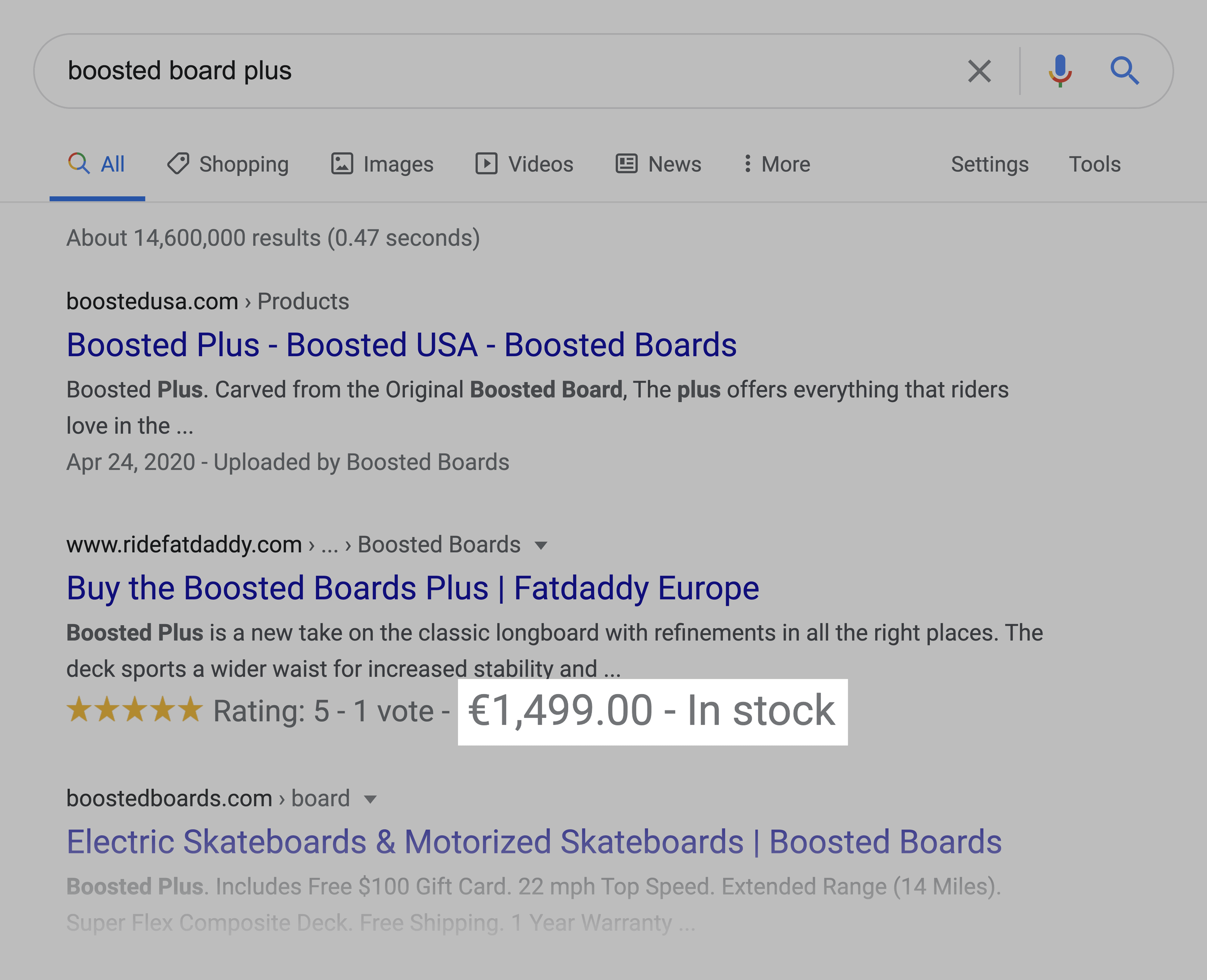
So if you’re shopping for a specific product, this can help you find the info you need without needing to hunt through a giant ecommerce product page.
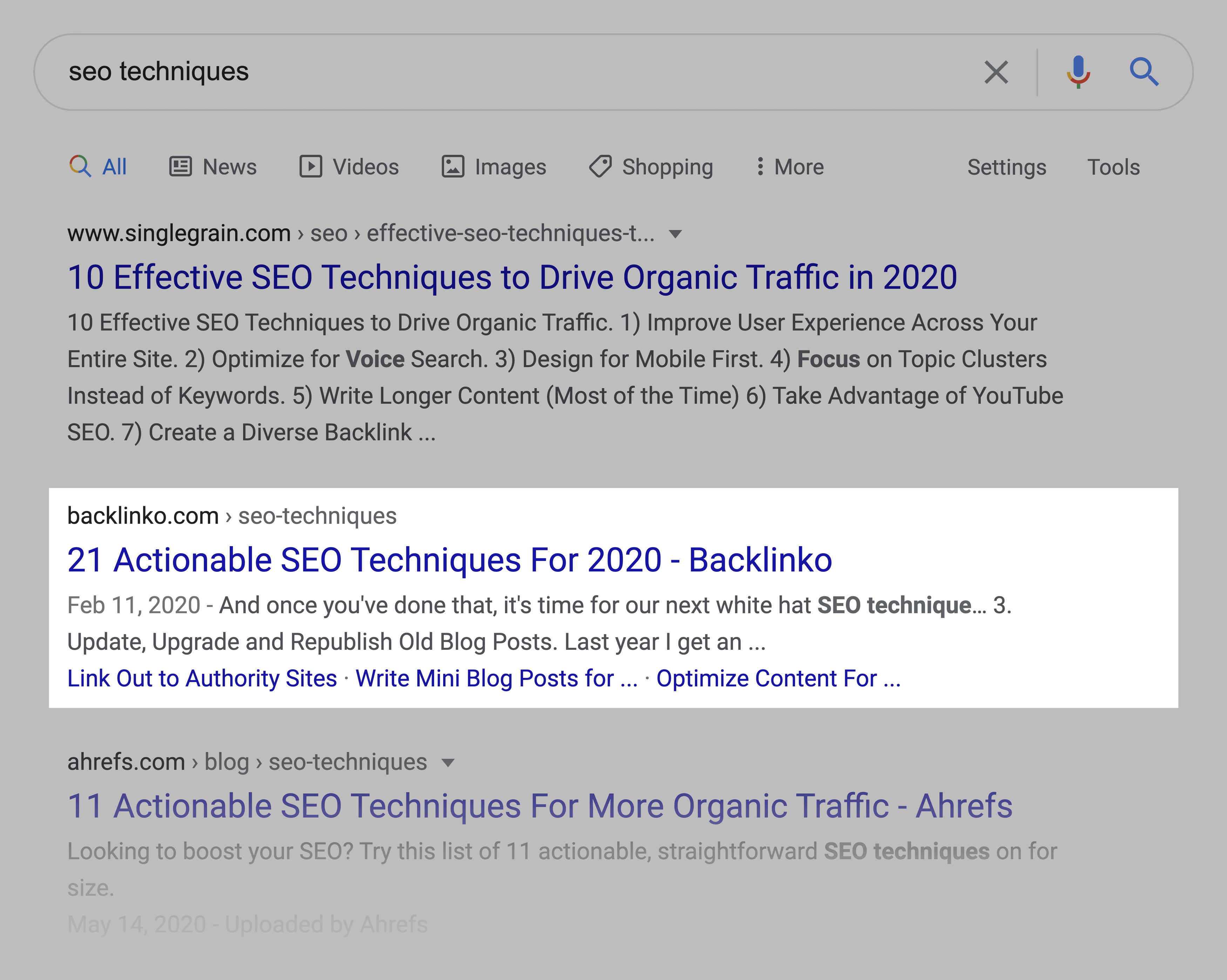
FAQ snippets are another common form of rich snippets.

Like any rich snippet, implementing structured data on your page can dramatically increase the odds of getting rich snippets.
5. Sitelinks
Sitelinks come in two main forms:
Links that take searchers to a page on a website.
Or those that take searchers to a section of a page.
Either way, sitelinks are designed to present a list of links underneath a traditional result. That way, users can jump directly to a page or content that they want to see.
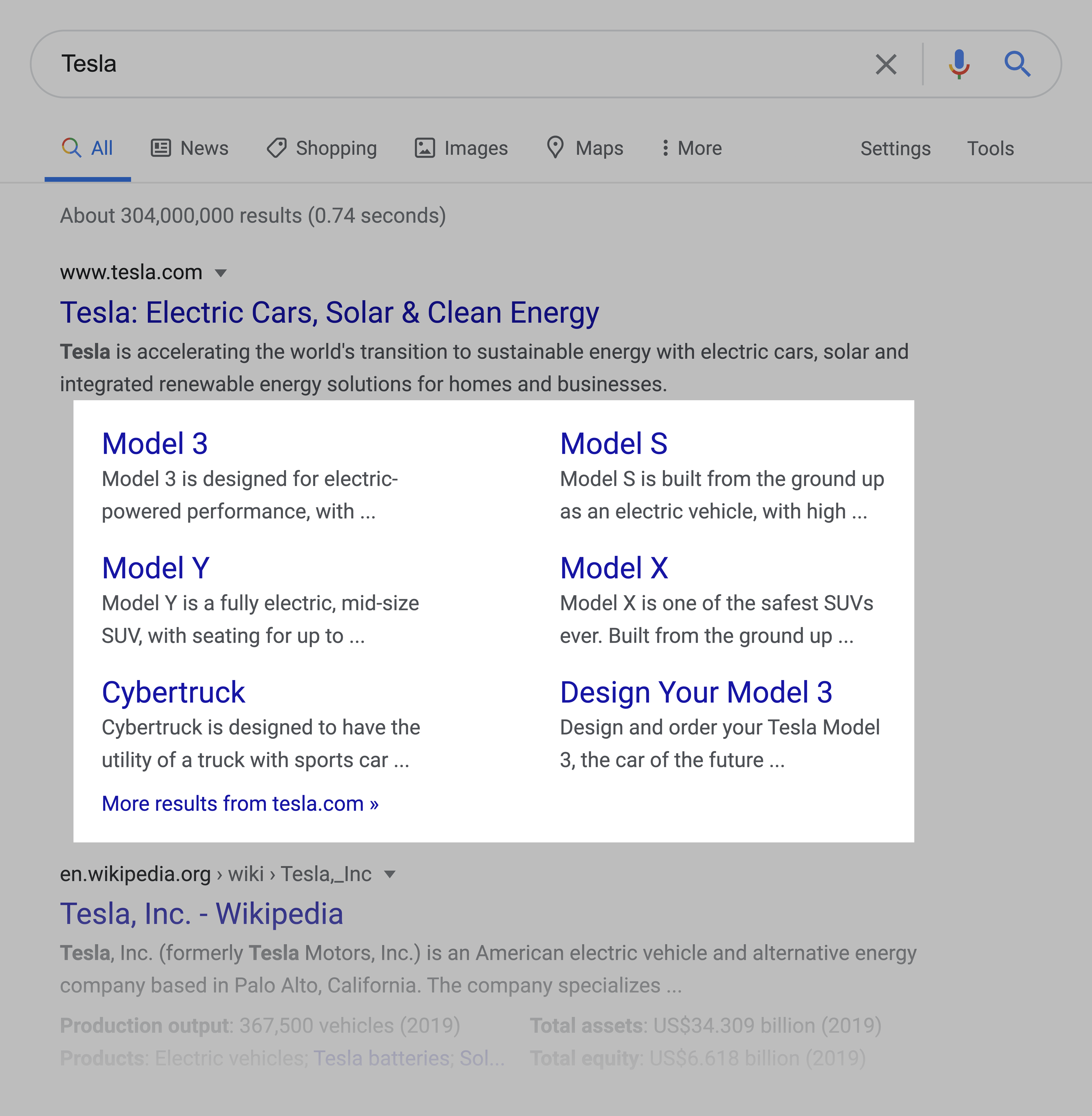
The most common forms of sitelinks are those that appear underneath a homepage for branded searches.

See why that’s helpful? If you search for “Tesla”, it can be hard for Google to understand exactly what you’re looking for from that site: the homepage? The about page? A page to login?
And sitelinks help you quickly find the page you want to visit.
It’s the same story with page-level sitelinks. They allow you to scan the main sections of a page. And, when you click, you’re taken to that section of the content.
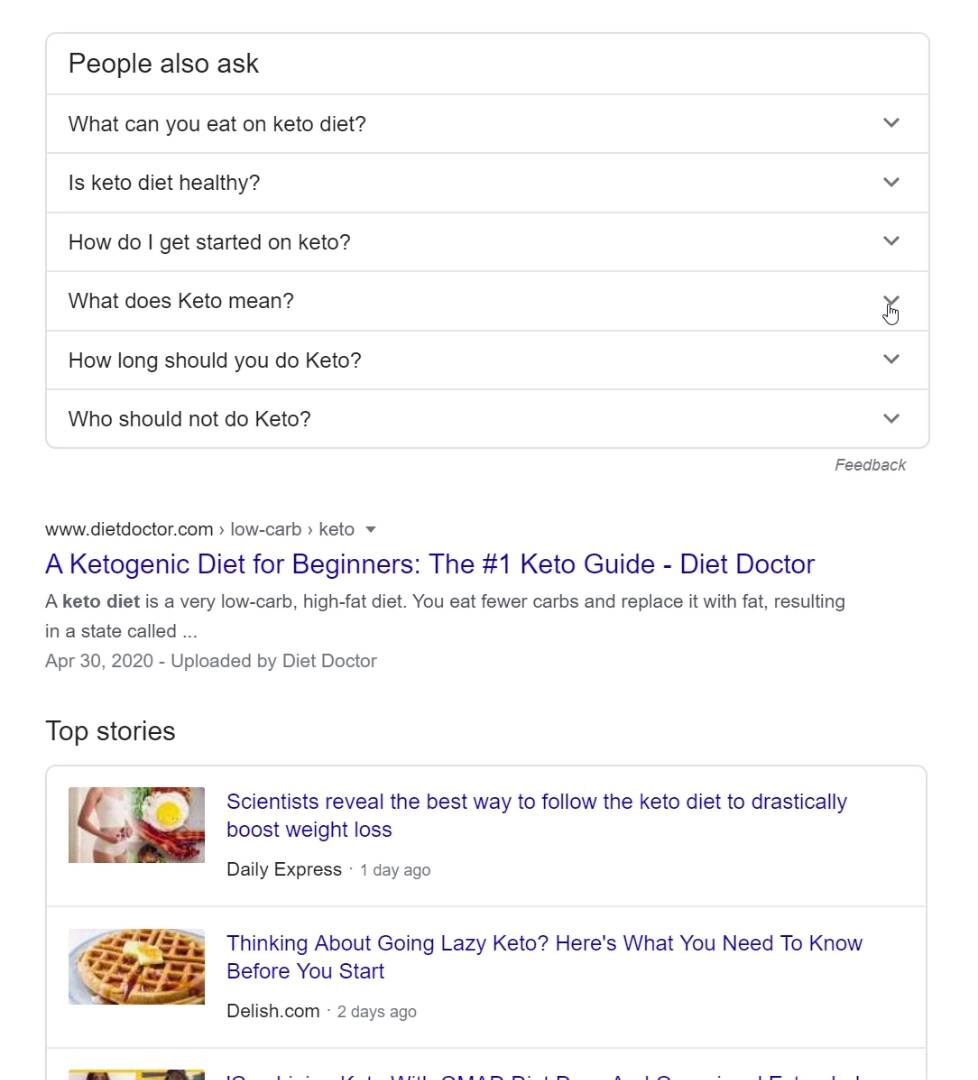
6. People Also Ask Boxes
According to Advanced Web Ranking, People Also Ask (PAA) boxes show up in 8.5% of all US-based search queries.
You’ve likely seen PAA boxes before. They’re essentially mini FAQs embedded in the organic search results.

And when you click on them, they expand with an answer. And generate more related questions.
Google’s goal with PAA is to give users an easy way to find answers to their next query… before they even search for it.
For example, the keyword “tennis backhand” brings up a PAA box.

As you can see, the PAA is designed to answer the question that person might want an answer to right then. Or one that he or she would search for next.
7. Local Packs
Local Packs (also known as “The Map Pack”) are a set of 3 local results that shows up for a query that Google considers “local”.
(For example, “barber Boston” or “barber near me”).
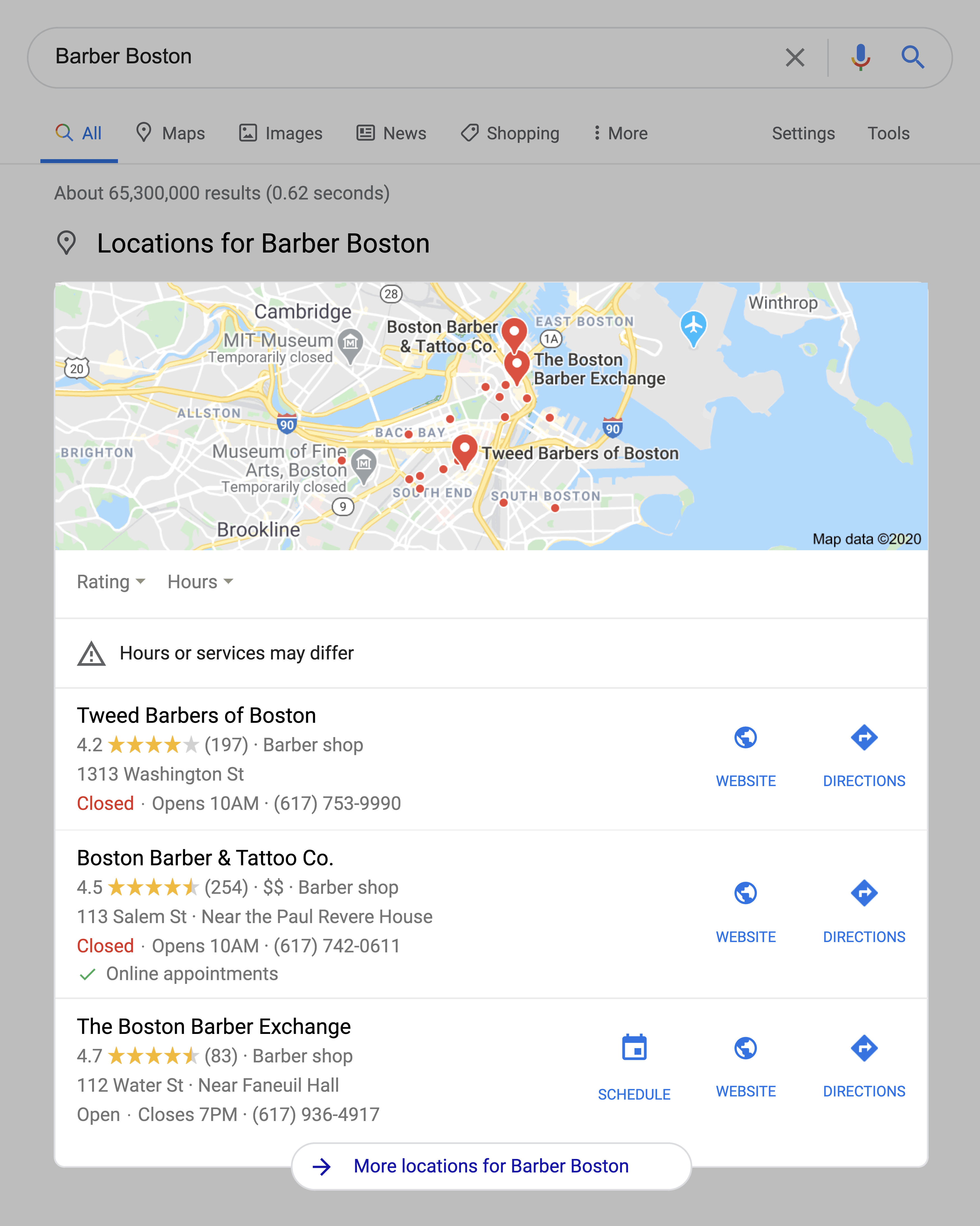
What’s unique about local packs is that they kind of have their own parallel algorithm. While many of Google’s ranking factors are focused on backlinks, local SEO is more about optimizing your Google My Business profile, getting good reviews and accurate NAP citations.
Regardless, local packs are super important for local businesses. Or businesses with a physical location.
That’s because local packs usually appear prominently in the search results. They also contain an interactive Google Maps map. Plus, other visual elements that help it stand out from the other organic Google search results.
8. Knowledge Panels
Knowledge Panels are featured snippet-type boxes that display data that Google has on a specific entity (like a famous person, company, or event).
Here’s an example of a Knowledge Card:
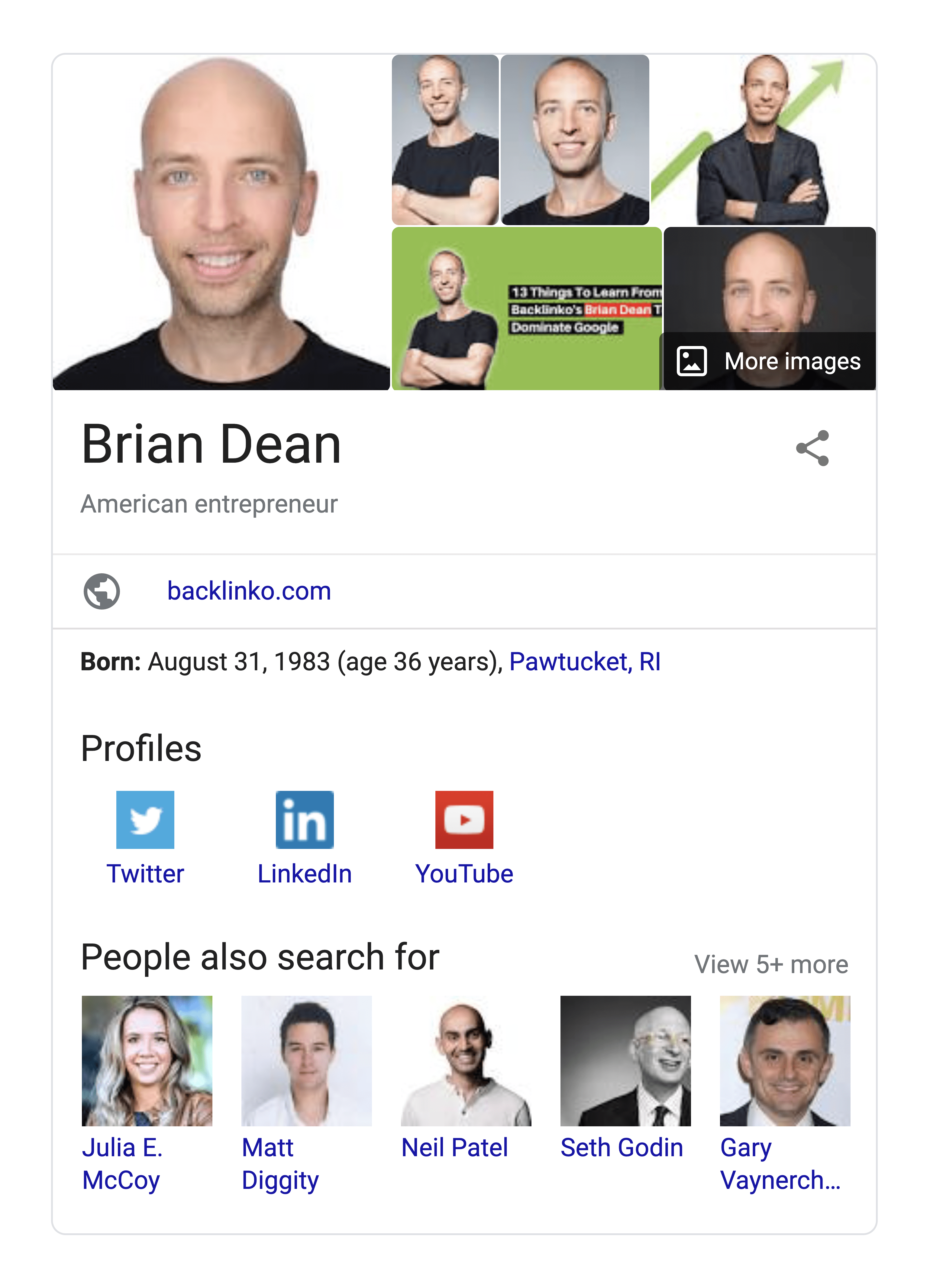
What makes Knowledge Panels different from featured snippets is that the data isn’t pulled from a specific webpage. Instead, Google gets the information from The Google Knowledge Graph.The Knowledge Graph itself is sourced from a variety of sources, like Wikipedia.
9. Image Packs
An image pack is a series of images that Google displays in the search results.
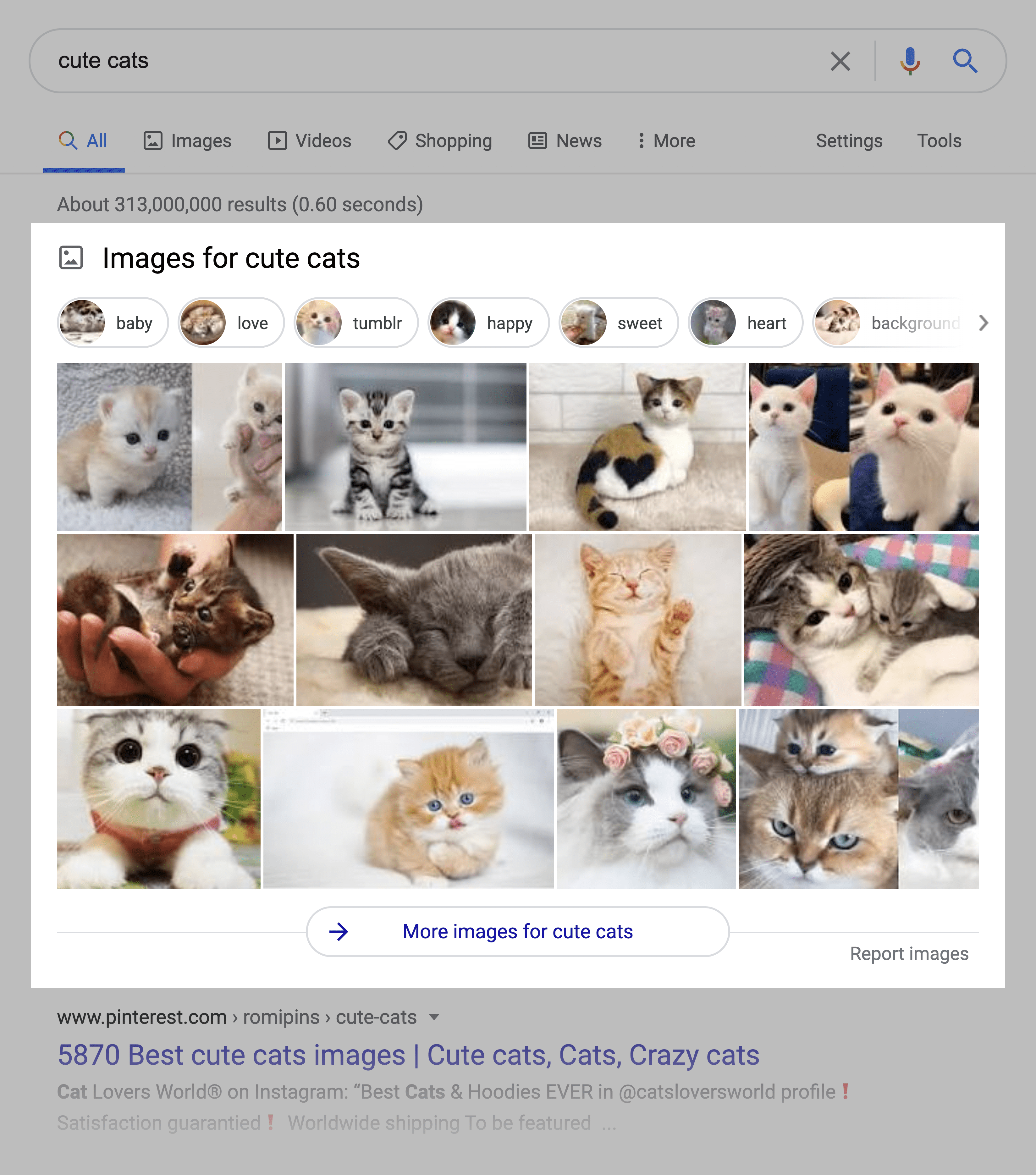
(Those images come from Google Images).
In other words, Google identifies search queries where users want to see a set of images. Sometimes, these queries are obvious (like “pictures of cats”). But other times,
Google is able to figure out which queries should have an image pack based on user behavior. That’s why image SEO is so important.
For example, take a keyword like “press release”. You may not expect that search to bring up an image pack. But it does.
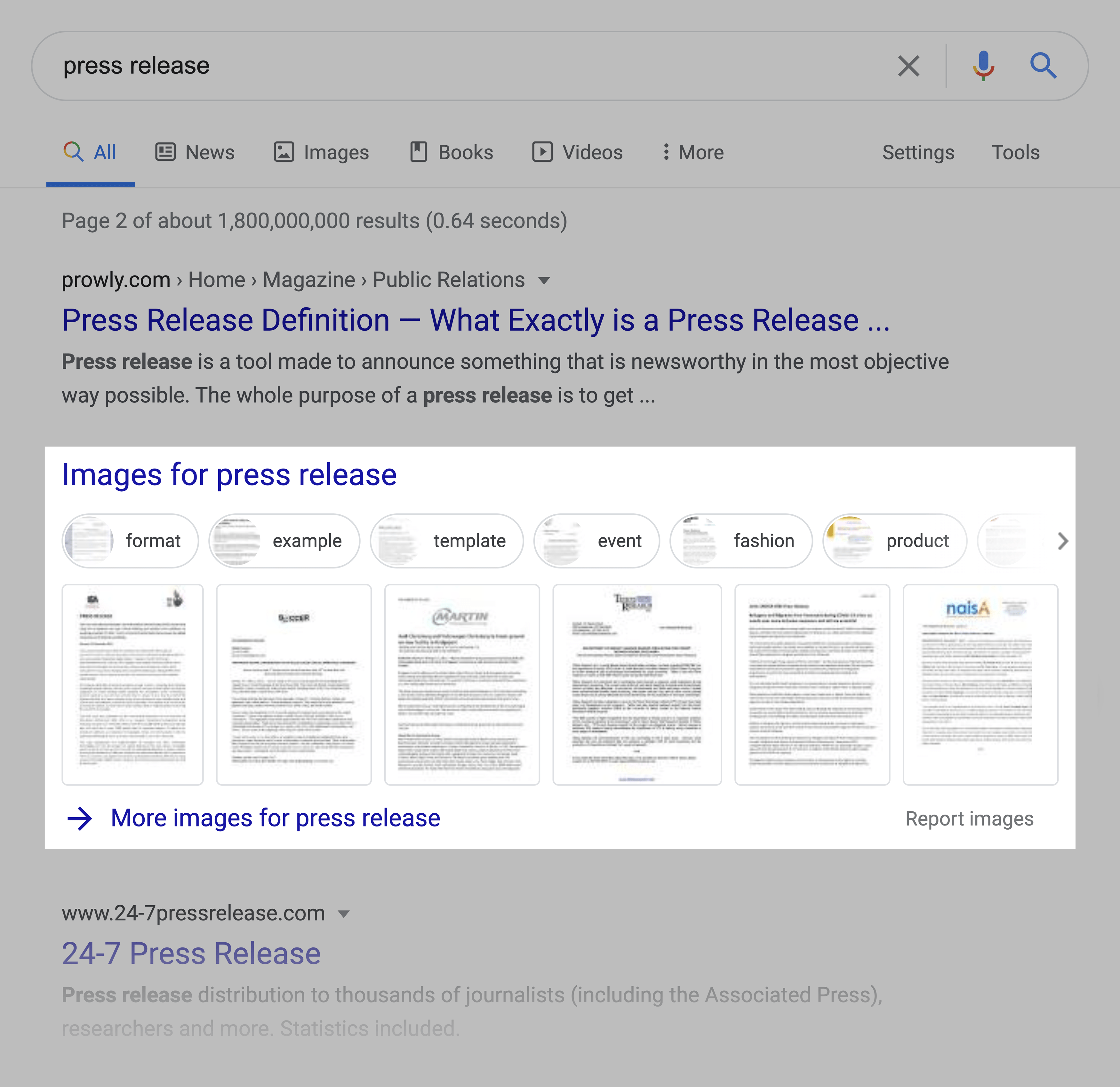
That’s likely because Google has tested the results with and without an image pack. And the search results with an image pack gave searchers what they wanted. So they decided to show it by default moving forward.
(Note: Google’s AI algorithm, RankBrain, executes this exact process for all queries. Not just those involving image packs. But this is a great example of how this system works).
10. Twitter Cards
Google indexes Twitter. And they tend to show a Twitter card when you search for something that a lot of people are talking about on Twitter.
They also show Twitter cards when you search for certain entities (like people or brands).
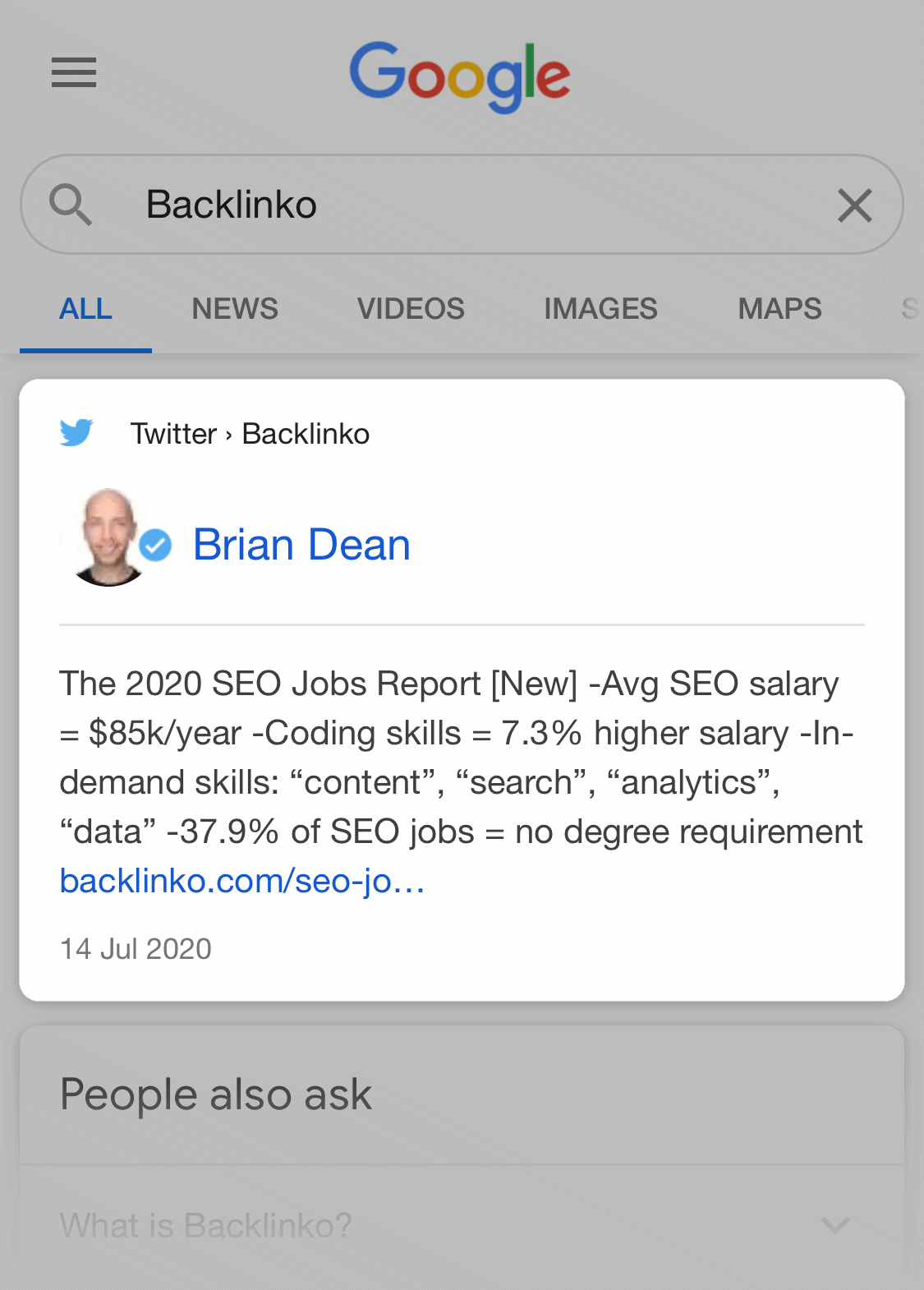
As you can see, Google isn’t just displaying a link to someone’s Twitter account. It’s an interactive SERP feature that lists out the user’s recent tweets.
11. Top Stories
Top stories are results that show up for terms related to a trending news story.
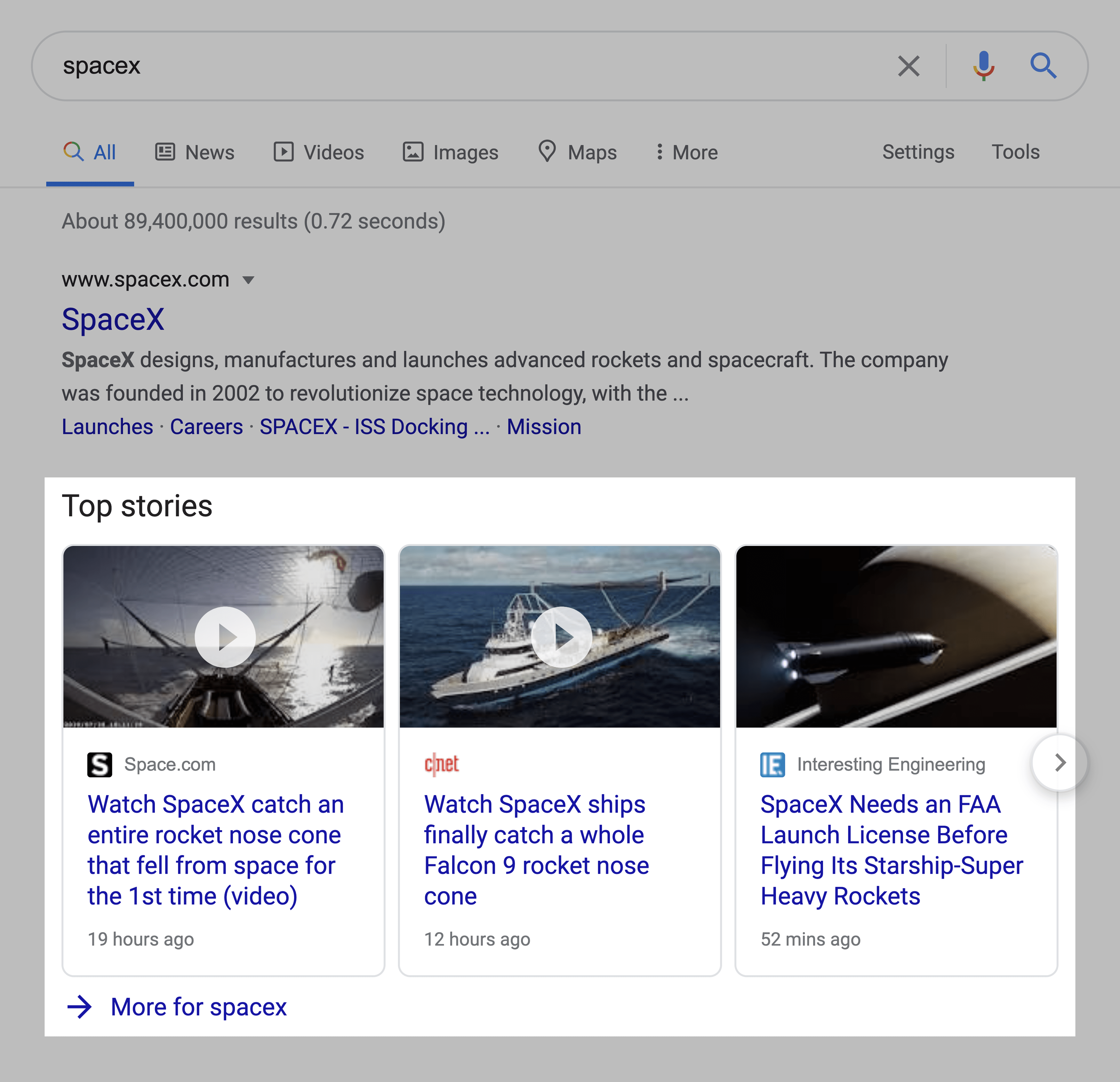
This SERP feature works similarly to Twitter cards. Google keeps track of trending stories (specifically, in Google News). And understands when a search matches a story that’s getting lots of traction.
The difference is that Google can technically pull any Tweet into a Twitter card. But with Top Stories, 100% of the results in the news box are from Google News approved websites.
Learn More
Getting Started With Schema: Helpful guide for learning the ins and outs of schema markup. Which is super important if you want rich snippets.
How to Get More Google Traffic in 2020: Video tutorial that shows you ways that you can get more Featured Snippet rankings.
The Definitive Guide to On-Page SEO: Solid on-page optimization can help Google find, index and understand the content of your page. All of which can help your site get rich snippets. Or show up as part of a SERP feature.